
The quest for the perfect LCD display can be a perplexing journey. As a business, you have unique needs—whether it’s for outdoor readability, energy efficiency, or sharp color accuracy. So, you’re probably wondering which display technology—Transmissive, Reflective, or Transflective—aligns with your specific requirements.
If we’re talking about tailored suitability, Transmissive displays excel indoors and offer vivid colors, Reflective displays are best for high ambient light conditions, and Transflective displays offer a middle-ground solution that’s versatile but less vibrant.
Curious to dig deeper? Stick around as we dissect the intricacies and potential business applications for each type.
Related: What is LCD ( Liquid Crystal Display ) ?
What Are Transmissive Displays?
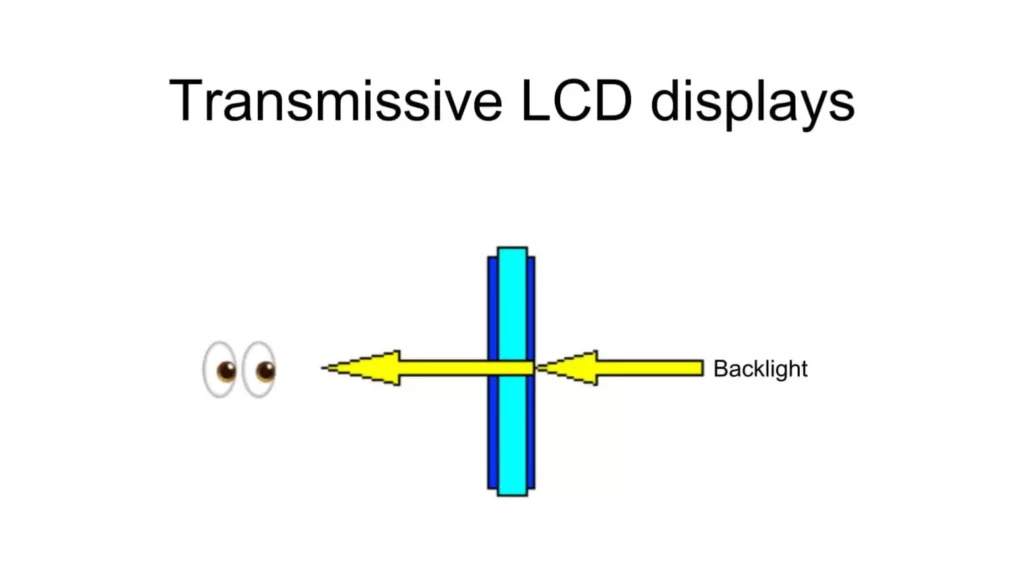
Transmissive displays are designed to be used primarily in controlled lighting conditions. They are commonly found in indoor settings like offices, malls, and homes.
How Does It Work?
In a Transmissive display, a backlight illuminates the pixels on the screen. Layers of liquid crystals control the light that passes through each pixel. The light travels through these layers to generate the color and brightness we see. The backlight stays on to ensure consistent illumination across the display.
In-Depth: The consistent backlighting provides high color accuracy and wide viewing angles but also results in higher power consumption.
Pros:
- High Color Accuracy: Transmissive displays are known for their excellent color reproduction. This makes them ideal for applications like digital design and medical imaging where color fidelity is critical.
- Adjustable Brightness: The backlighting in Transmissive displays is adjustable, allowing for easier readability in various lighting conditions.
- Wide Viewing Angles: These displays offer wide viewing angles, making them suitable for applications where the screen will be viewed from different directions.
Cons:
- High Power Consumption: These displays require a constant power source for the backlight, making them less energy-efficient.
- Poor Outdoor Visibility: Without an external light source, these displays are difficult to read in direct sunlight.
Transmissive displays are widely used in control rooms, digital signage, and medical imaging where high-definition and color accuracy are crucial.
What Are Reflective Displays?
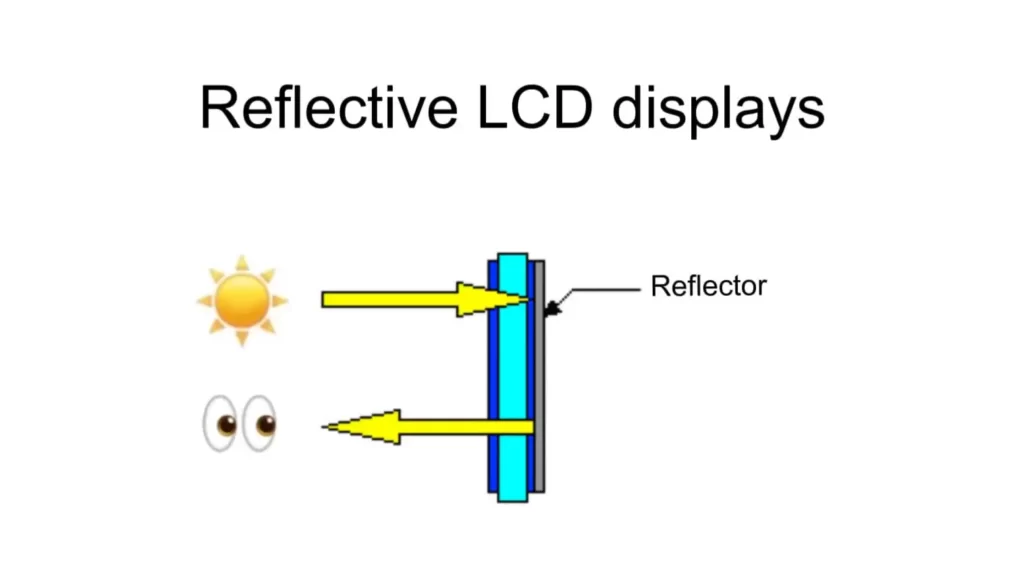
Reflective displays are engineered for outdoor and high ambient light conditions. They are often found in devices used in fieldwork, like handheld GPS units and industrial machinery.
How Does It Work?
These displays operate without a backlight. Ambient light hits the screen and is reflected back, creating the image you see. Liquid crystals control this reflected light to form the images and text displayed.
In-Depth: The absence of backlighting allows these displays to be more energy-efficient. They perform best in well-lit conditions and might suffer visibility issues in low light.
Pros:
- Energy Efficiency: Reflective displays consume less power since they utilize ambient light. This is particularly useful for battery-powered devices.
- Excellent Outdoor Readability: Because they use ambient light, they perform exceptionally well in bright outdoor settings.
- Lower Cost: Generally, Reflective displays are more budget-friendly compared to Transmissive displays.
Cons:
- Limited Color Range: These displays usually have a more restricted color palette, making them unsuitable for applications requiring high color accuracy.
- Dependence on External Light: In low-light conditions, visibility can be a challenge without an external light source.
Industries like construction and agriculture often use Reflective displays due to their durability and outdoor visibility.
What Are Transflective Displays?
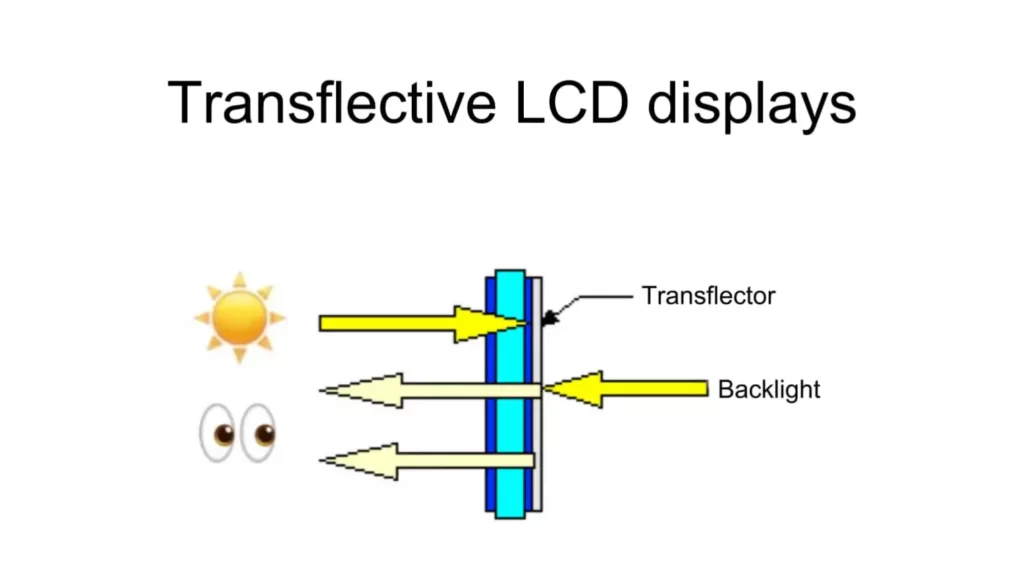
Transflective displays offer a compromise between Transmissive and Reflective technologies. They are versatile and can be used in both indoor and outdoor settings.
How Does It Work?
Transflective displays utilize both a backlight and ambient light. In bright conditions, they use external light to make the screen visible. In darker settings, a backlight provides the necessary illumination.
In-Depth: This dual operation allows for versatility, though it often results in a slight compromise in terms of color vibrancy when compared to purely Transmissive displays.
Pros:
- Versatility: Transflective displays are adaptable to both indoor and outdoor environments, making them a flexible choice.
- Moderate Power Consumption: While not as energy-efficient as Reflective displays, they do offer a middle-ground in terms of power usage.
- Balanced Features: They offer a compromise between the color accuracy of Transmissive displays and the energy efficiency of Reflective displays.
Cons:
- Compromised Color Vibrancy: While versatile, the color vibrancy is not as high as that of Transmissive displays.
- Cost: These displays can sometimes be pricier than Reflective displays but cheaper than high-end Transmissive displays.
These displays are often seen in automotive applications and portable devices.
Related: What is LED Backlight?
How Do I Choose? An In-Depth Guide
Choosing the right LCD display technology is a multi-faceted decision that depends on various factors. Here’s a more detailed breakdown to guide your choice:
Assess the Operating Environment
The environment where your display will operate is crucial.
- Indoor Applications: If you’re looking for displays that will mainly be used indoors, Transmissive displays with their better color reproduction and adjustable brightness are the way to go. For example, they’re often found in retail signage and point-of-sale (POS) systems.
- Outdoor Applications: Reflective displays excel in outdoor conditions where ambient light can be leveraged for better visibility. These are seen in devices used for fieldwork, like GPS units in agriculture.
- Mixed Use: If your application involves both indoor and outdoor settings, consider Transflective displays for their versatility.
| Features | Transmissive | Reflective | Transflective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best for | Indoor/Low-light | Outdoor/High-light | Versatile |
| Power Consumption | High | Low | Moderate |
| Visibility | Excellent in low light | Excellent in high light | Good in varied light |
Evaluate Power Consumption Needs
How long your display needs to run and what sort of power resources you have are significant considerations.
- Energy Efficiency: If you’re trying to minimize energy costs or require a battery-operated solution, Reflective displays are a better fit.
- No Power Constraints: If power consumption isn’t a concern, Transmissive displays can offer better features at the expense of higher energy use.
Consider Color and Brightness
Your application might require different levels of color accuracy and brightness.
- High Color Accuracy: If you’re in design, medical imaging, or any field where color differentiation is critical, Transmissive displays should be your pick.
- Basic Display: In contrast, if you’re displaying basic text or monochrome graphics, a Reflective display will suffice.
Budget Constraints
All these technologies come at different price points. Transmissive displays tend to be costlier due to the complex backlighting system, while Reflective and Transflective displays can be more budget-friendly.
Consult the Experts
If in doubt, it’s always a good idea to consult with experts in the field. Many companies offer consultations to help tailor a solution specific to your business needs. Start by contact with experts.

More Related Questions
Are these technologies evolving?
Absolutely. With the advent of better materials and techniques, all three types of displays are undergoing constant innovation.
Can I customize these displays?
Yes, many manufacturers offer custom solutions tailored to your business needs. Check out custom display sulotion.
Conclusion
Choosing between Transmissive, Reflective, and Transflective displays boils down to your business needs—whether it’s color vibrancy, energy efficiency, or versatility. Make a checklist of your priorities, and you’ll be well on your way to making a decision that enhances your operations.











